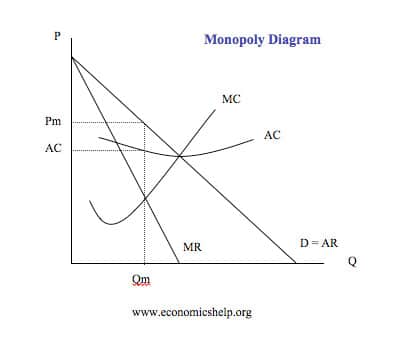
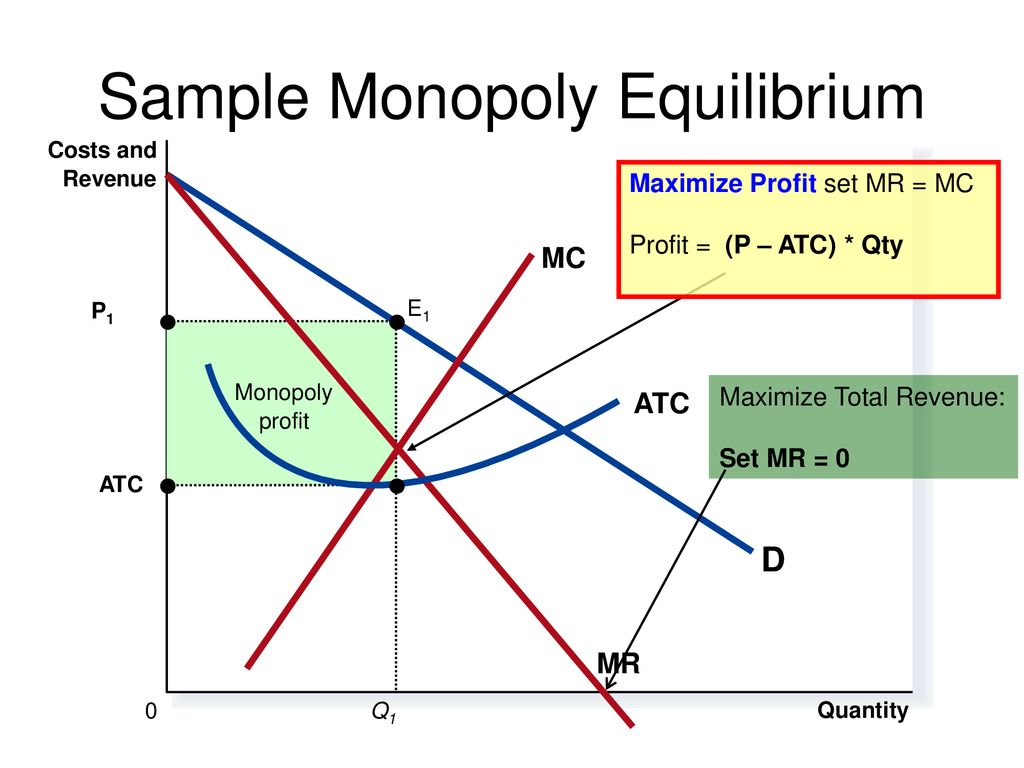
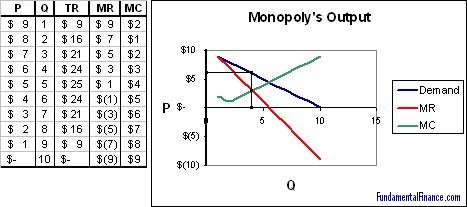
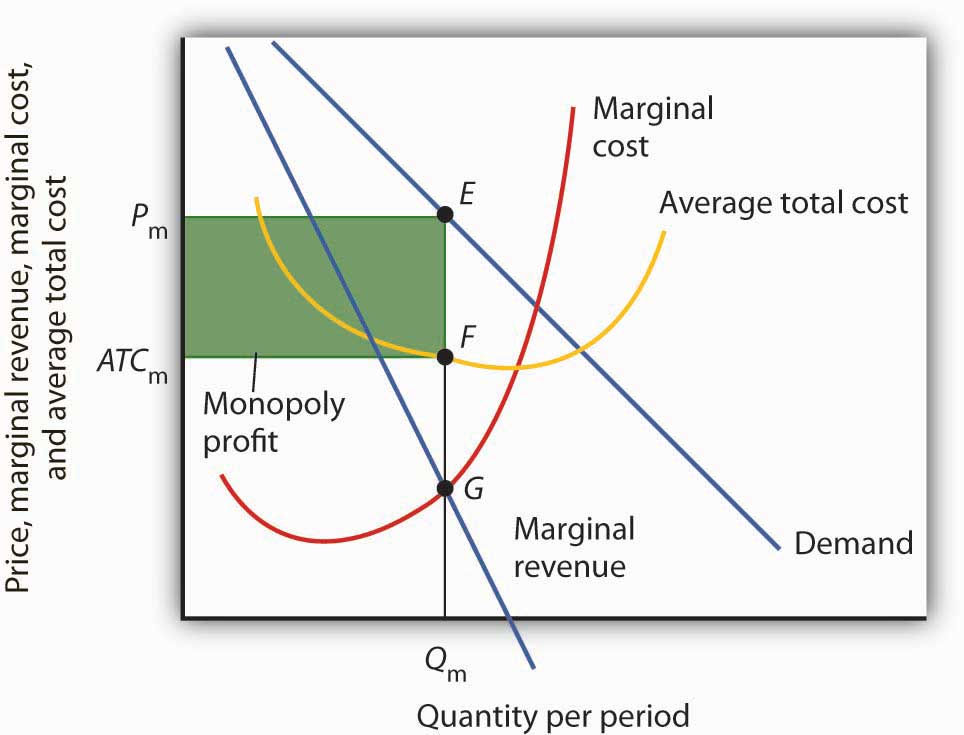
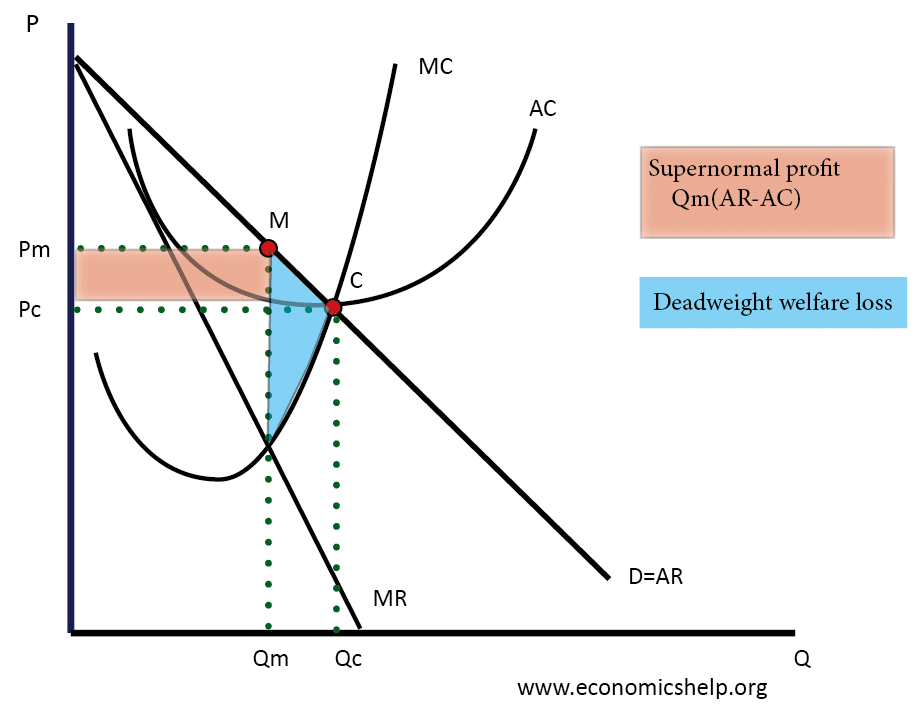
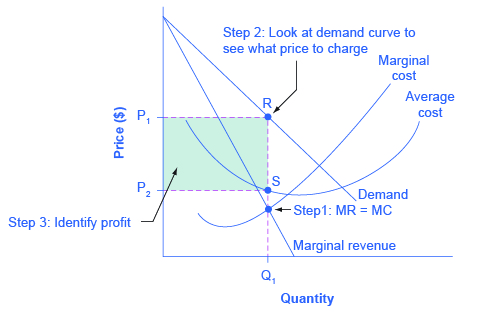
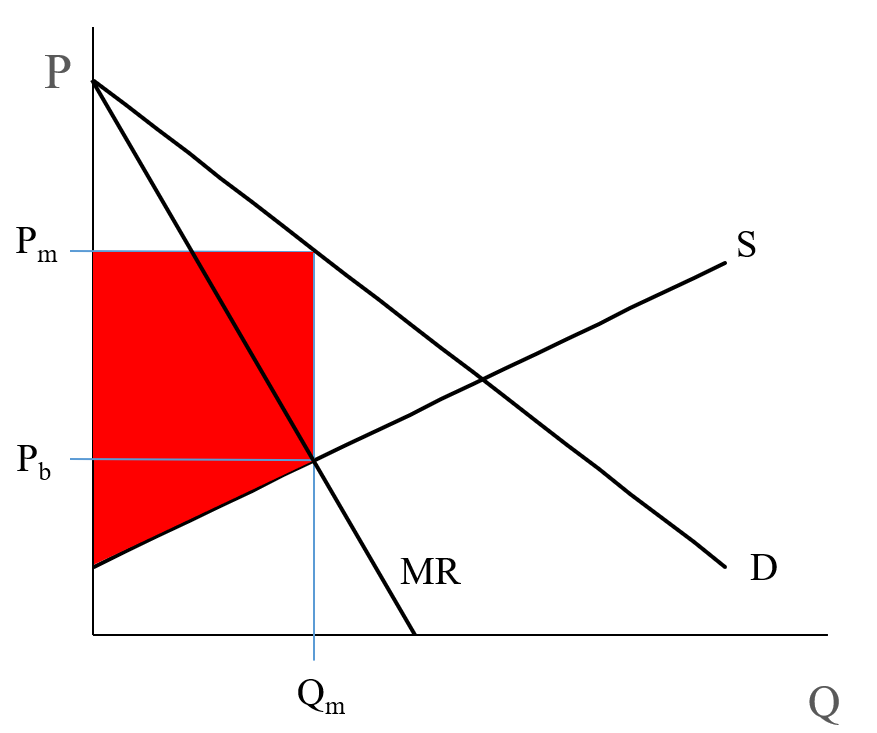
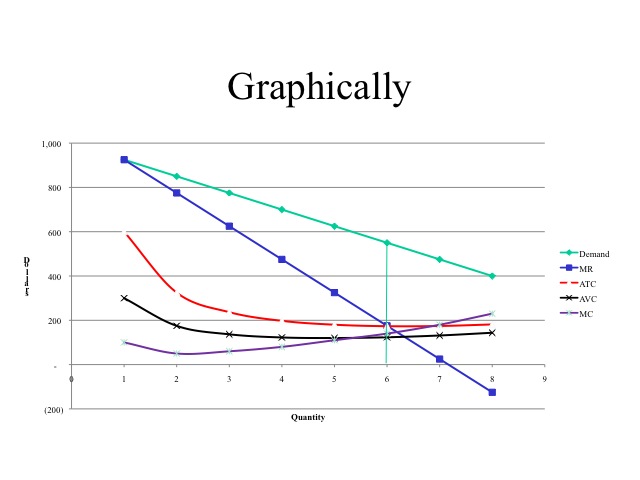
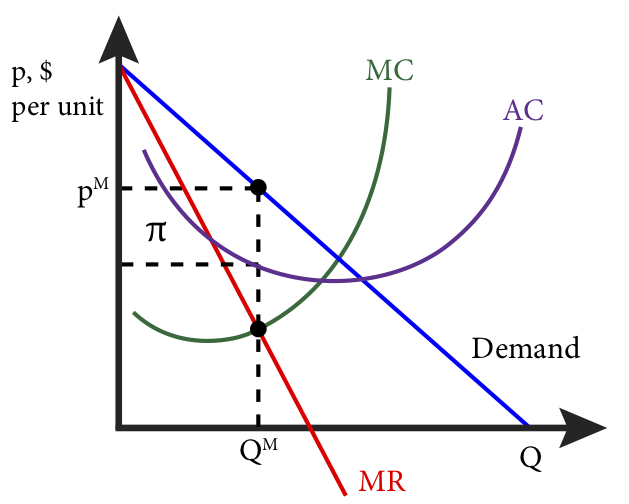
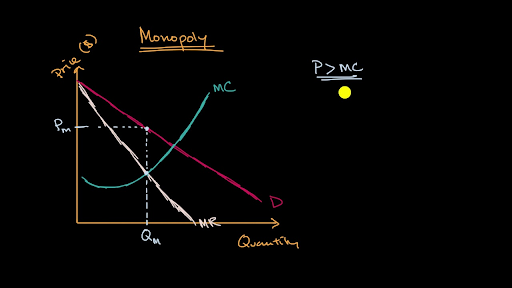
Illustrate the MR = MC rule for a monopoly and show why, over the short run, it will always make economic profit. List at least one (1) reason why economic profit is
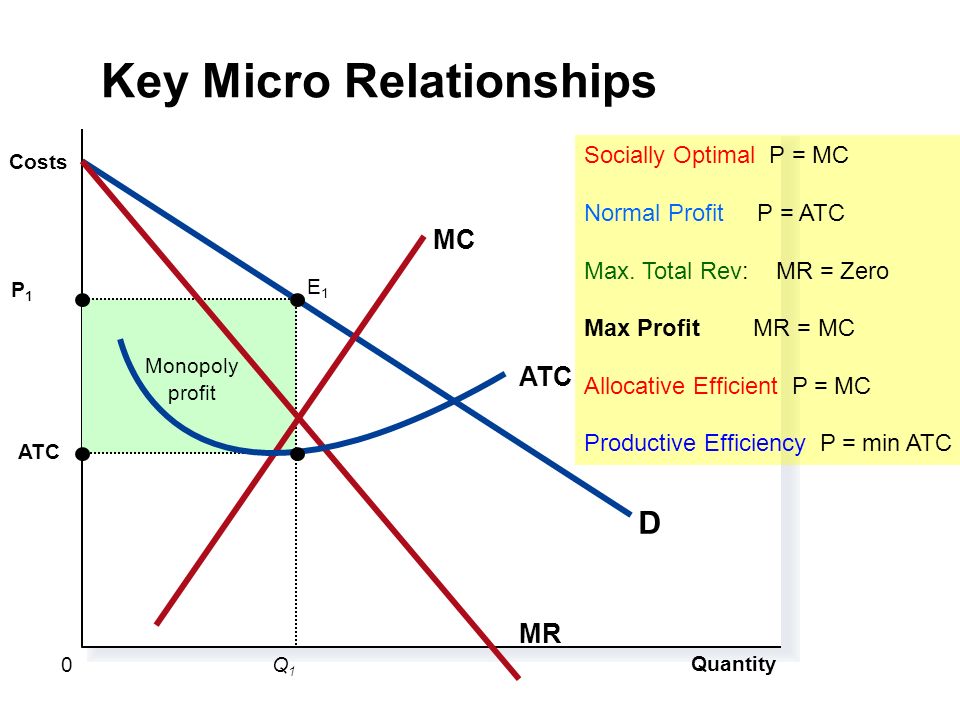
Monopoly profit ATC Quantity P 1 Q1Q1 0 Costs D MR MC ATC E1E1 Key Micro Relationships Socially Optimal P = MC Normal Profit P = ATC Max. Total Rev: MR. - ppt download
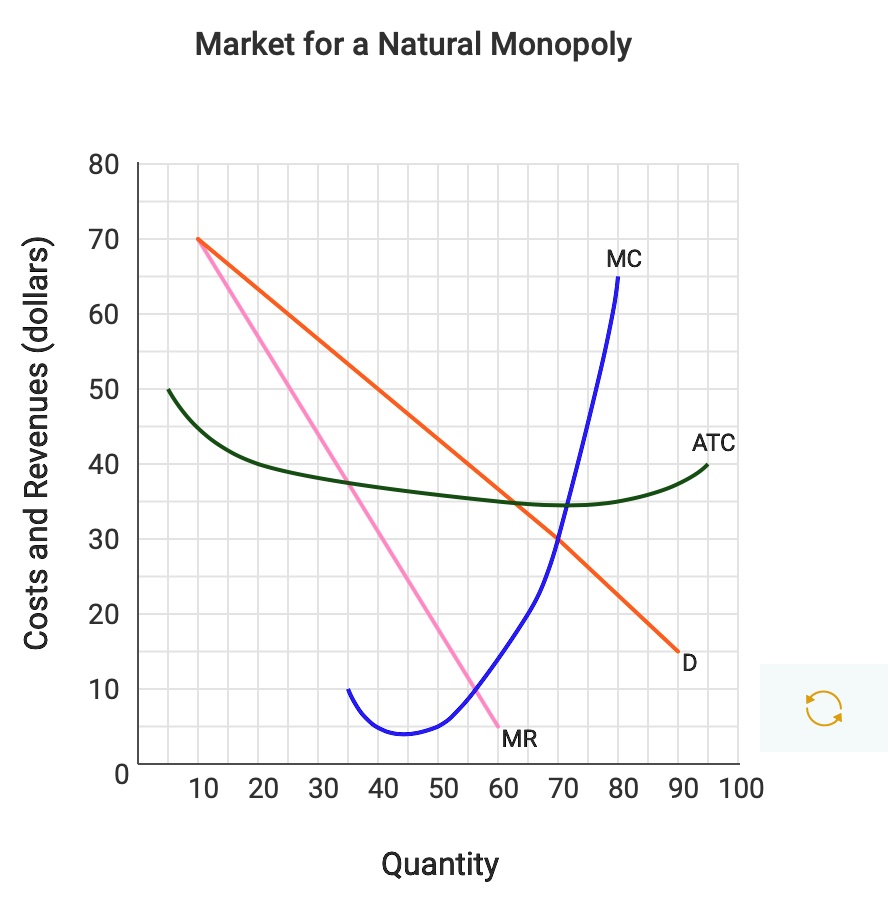
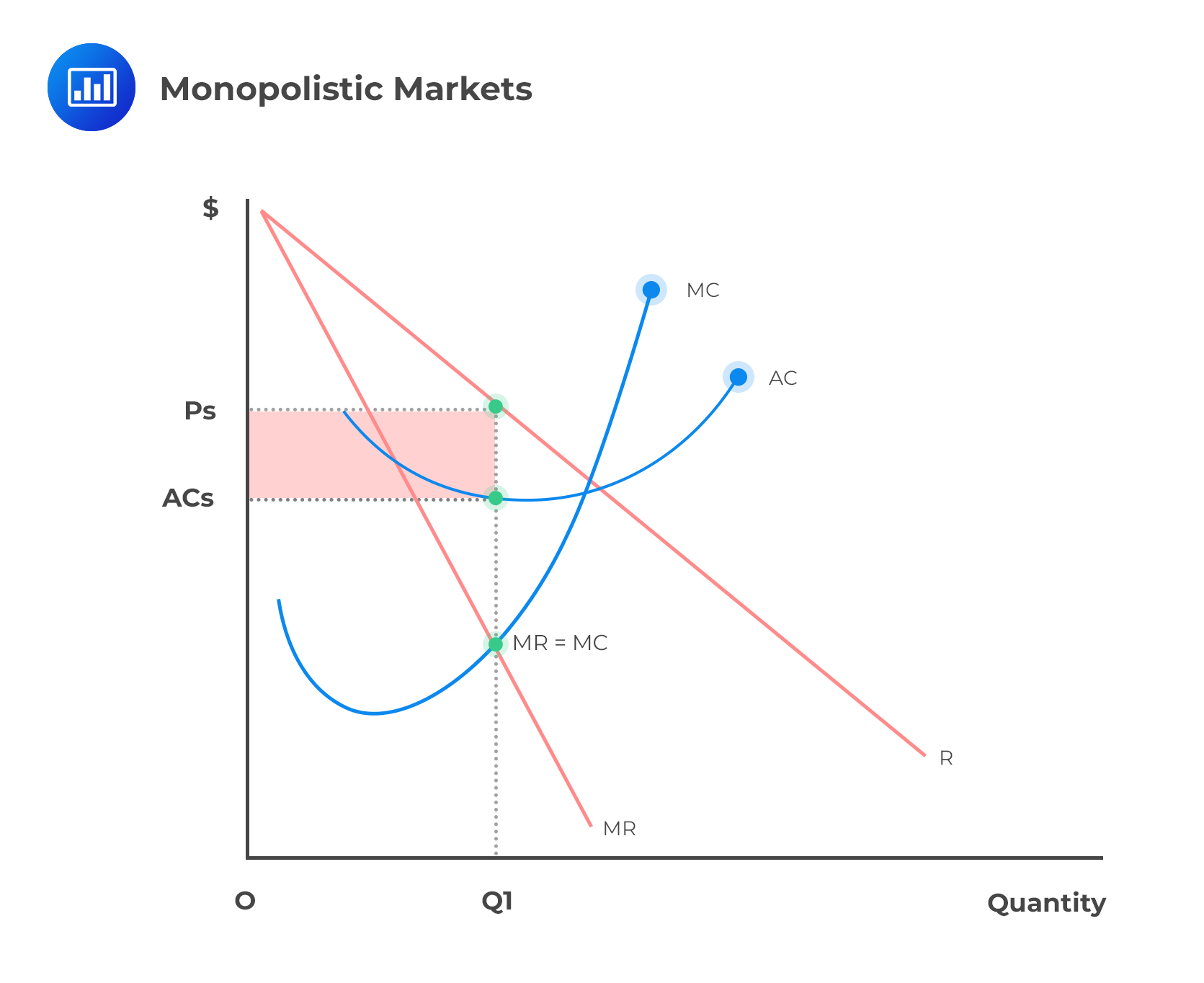
SOLVED: The following graph depicts the demand (D), marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), and average total cost (ATC) curves for a firm operating as a natural monopoly. a. If the firm

Give a graphical representation of the MC, ATC, MR, and demand curves of a monopolist. | Homework.Study.com

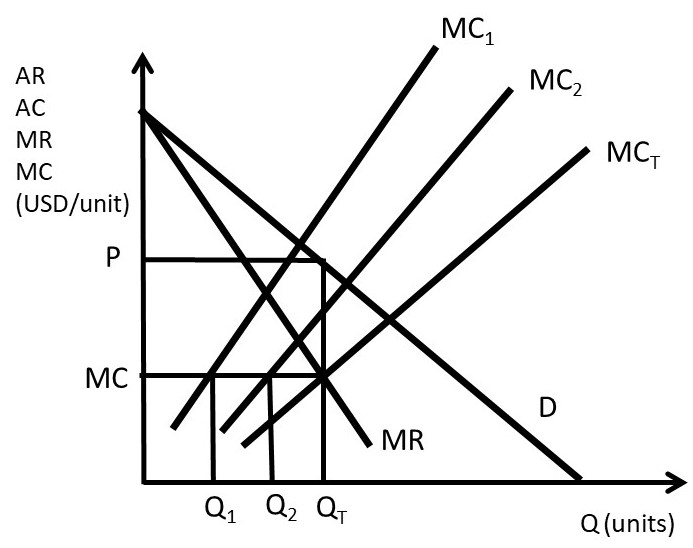

![Unit 9: Monopoly | Econproph [Micro] Unit 9: Monopoly | Econproph [Micro]](http://micro.econproph.net/files/2012/08/monopoly-D-MR-MC1.png)